ANALYSIS – It's really dark out there! Dark energy and dark matter make up 95% of the universe, but scientists don't know much about them. NASA is working on its ‘Nancy Grace Roman' space probe to find answers in the vast dark.
It is expected to launch in May 2027.
Meanwhile, the European Space Agency (ESA) – their equivalent to NASA – is launching its ‘Euclid' space telescope next week to uncover the dark universe and explore its evolution over the past 10 billion years.
Together they will complement each other's efforts.
NASA says the two missions' surveys will overlap, with Euclid likely observing the whole area Roman will scan. It adds:
“Euclid's first look at the broad region of sky it will survey will inform the science, analysis, and survey approach for Roman's deeper dive,” said Mike Seiffert, project scientist for the NASA contribution to Euclid at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
Euclid is scheduled to launch on July 1 on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral, Florida, and then begin its mission of studying the mysteries of dark energy and matter.
NASA's Roman space telescope will join Euclid much later and scientists will use its more sensitive and precise data to apply corrections to Euclid's and extend the corrections over Euclid's much larger area.
Dark energy and matter have proven incredibly elusive for the better part of a century.
Astronomers infer the existence of dark matter from the behavior of the stars and galaxies. The first hint of dark matter's existence came in 1933 when Swiss astronomer Fritz Zwicky calculated that the Virgo Cluster of galaxies didn't have enough visible mass in the form of gas and stars to hold it together.
There must be some invisible matter, or else it would fly apart, he argued.
“Dark energy and dark matter reveal themselves by the fairly subtle changes they make to the appearance of objects in the visible universe; otherwise, we don't know about them,” René Laureijs, Euclid project scientist, said in a live-streamed ESA briefing.
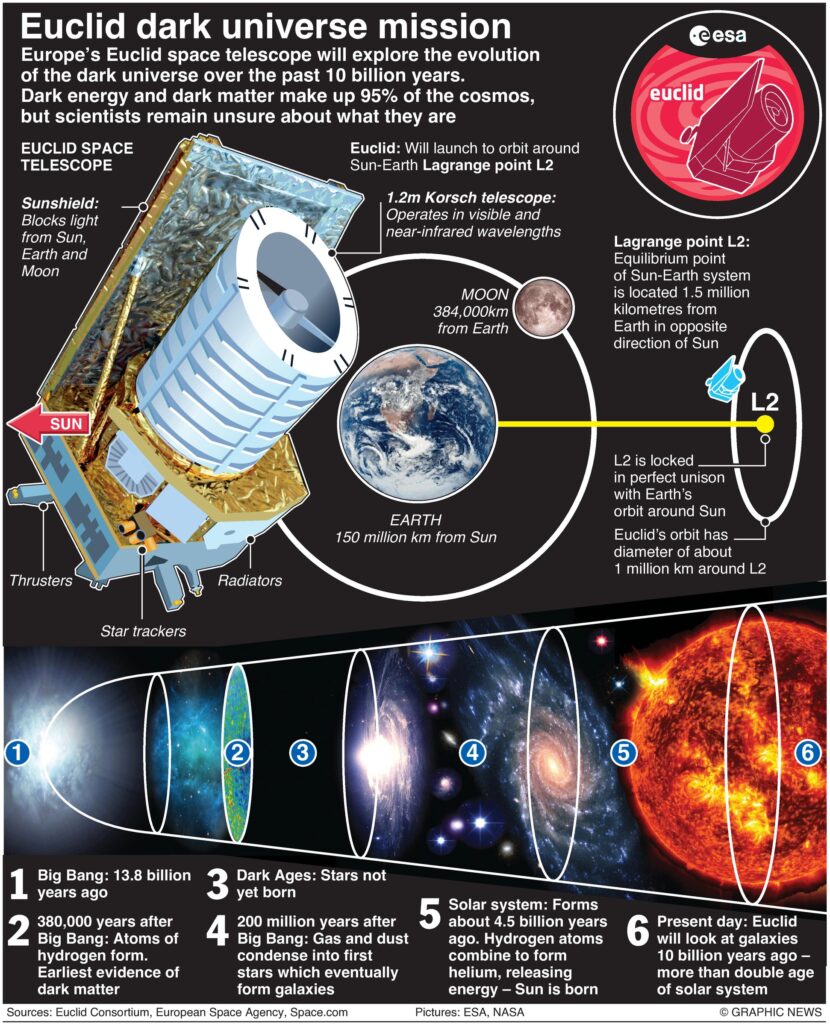
Euclid has two scientific instruments: a visible light camera to measure the shape of galaxies and a near-infrared camera/spectrometer to measure their brightness and distance. The two instruments will work together to infer where the dark matter may be lurking by charting its effects on visible objects.
Euclid's image quality will be at least four times sharper than ground-based telescopes.
In contrast, NASA's Roman probe is 4x heavier than Euclid and will focus only on the infrared spectrum.
According to NASA:
Euclid and Roman are both designed to study cosmic acceleration but using different and complementary strategies. Both missions will make 3D maps of the universe to answer fundamental questions about the history and structure of the universe. Together, they will be much more powerful than either one individually.
Euclid will observe a far larger area of the sky – approximately 15,000 square degrees, or about a third of the sky – in both infrared and optical wavelengths of light, but with less detail than Roman. It will peer back 10 billion years to when the universe was about 3 billion years old.
Roman's largest core survey will be capable of probing the universe to a much greater depth and precision, but over a smaller area – about 2,000 square degrees, or one-twentieth of the sky. Its infrared vision will unveil the cosmos when it was 2 billion years old, revealing a larger number of fainter galaxies. While Euclid will focus on cosmology exclusively, Roman will also survey nearby galaxies, find and investigate planets throughout our galaxy, study objects in the outskirts of our solar system, and much more.
The two can be compared below.
Hopefully, the two impressive space exploration efforts working in tandem will help us better see and understand what's in ‘the dark.'
The opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the positions of American Liberty News.
READ NEXT: Who Will Be The First GOP Contender To Leave The Presidential Race?



No mention of how long it will take to start getting data and images back after the 2027 launch. Any ideas?
Life was so much simpler when the 3 basic elements were air, water, and fire. And the earth was flat.
Sigh.
Vatican admits Galileo was right
7 November 1992
newscientist. com/article/mg13618460-600-vatican-admits-galileo-was-right/
In 1633, the Inquisition of the Roman Catholic Church forced Galileo Galilei, one of the founders of modern science, to recant his theory that the Earth moves around the Sun. Under threat of torture, Galileo – seen facing his inquisitors – recanted. But as he left the courtroom, he is said to have muttered, ‘all the same, it moves’.
Last week, 359 years later, the Church finally agreed. At a ceremony in Rome, before the Pontifical Academy of Sciences, Pope John Paul II officially declared that Galileo was right.
My Theory!
Dark Matter has no charge because it is the residual stuff left over from the original Matter/Ani-Matter explosion in the beginning. Enough positive changed material was left over to form everything that exists today.
Dark Energy also has no charge because it is mistaken for the force expanding the Universe.
The Universe expanding at a faster and faster rate in a vacuum is akin to a rock rolling downhill at a faster and faster rate. There is nothing to impede it.
Great article, Mr.Crespo! Imagine the Lord of all things who created this magnificence!